Aggregations
We will cover internal implementation of common aggregations in this document.
Frontend
TODO
Expression Framework
TODO
HashAggExecutor
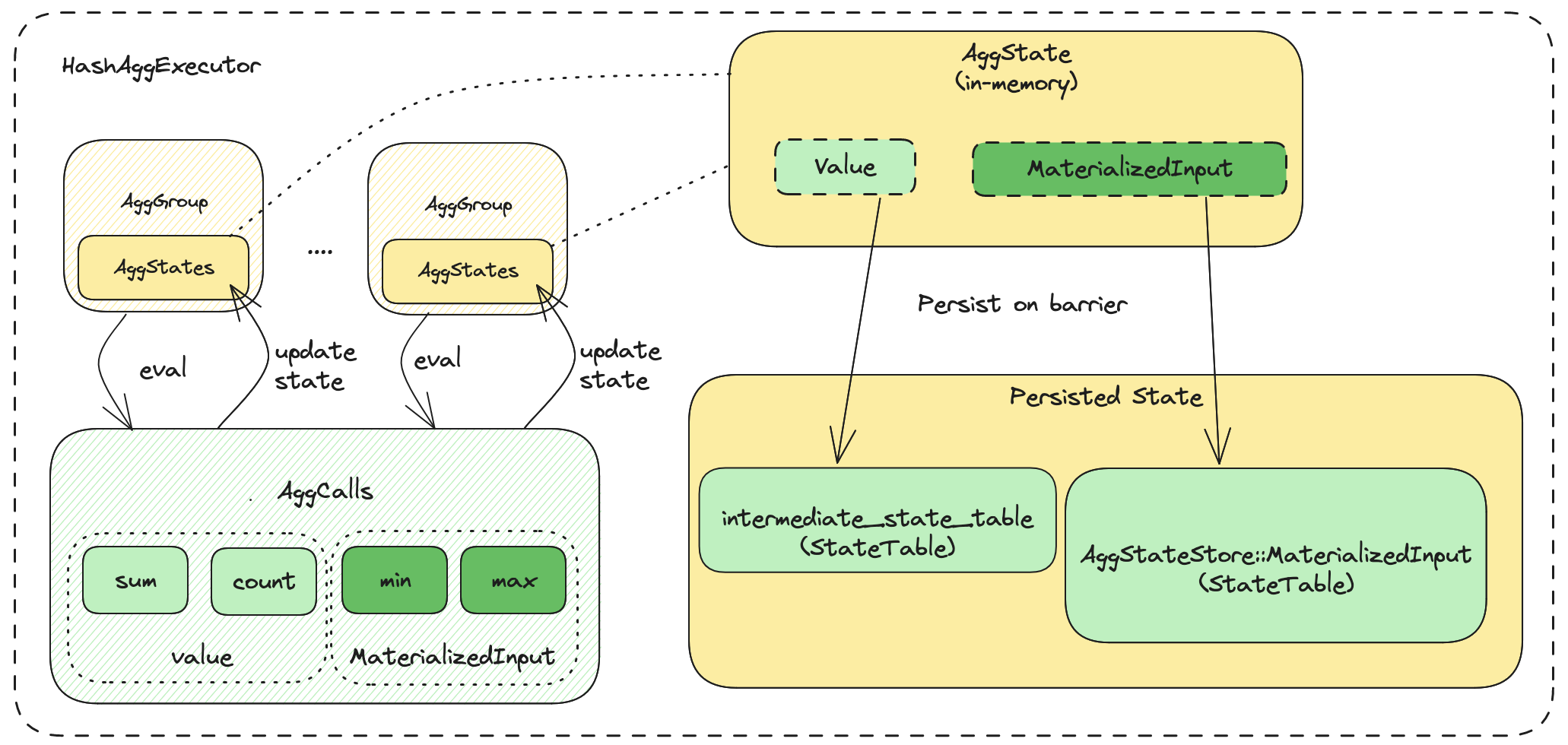
Within the HashAggExecutor, there are 4 main components:
- AggCalls.
- AggState.
- AggGroups.
- Persisted State.
AggCalls are the aggregation calls for the query. For instance SUM(v1), COUNT(v2) has the AggCalls SUM and COUNT.
AggState is the state we use to compute to the result (output) of the aggregation call. Within each aggregation group, it will have an AggState for each AggCall.
AggGroups are created per aggregation group.
For instance with GROUP BY x1, x2, there will be a group for each unique combination of x1 and x2.
Whenever stream chunks come in, the executor will update the aggregation state for each group, per agg call.
On barrier, we will persist the in-memory states.
For value type aggregations, we will persist the state to the intermediate state table.
This state table will store all value aggregations per group on a single row.
For MaterializedInput type aggregations, these require tracking input state. For example, non-append-only min/max.
For each of these aggregations, they have 1 state table (AggStateStorage::MaterializedInput) each. Within the state table, it will store the input state for each group.
Initialization of AggGroups
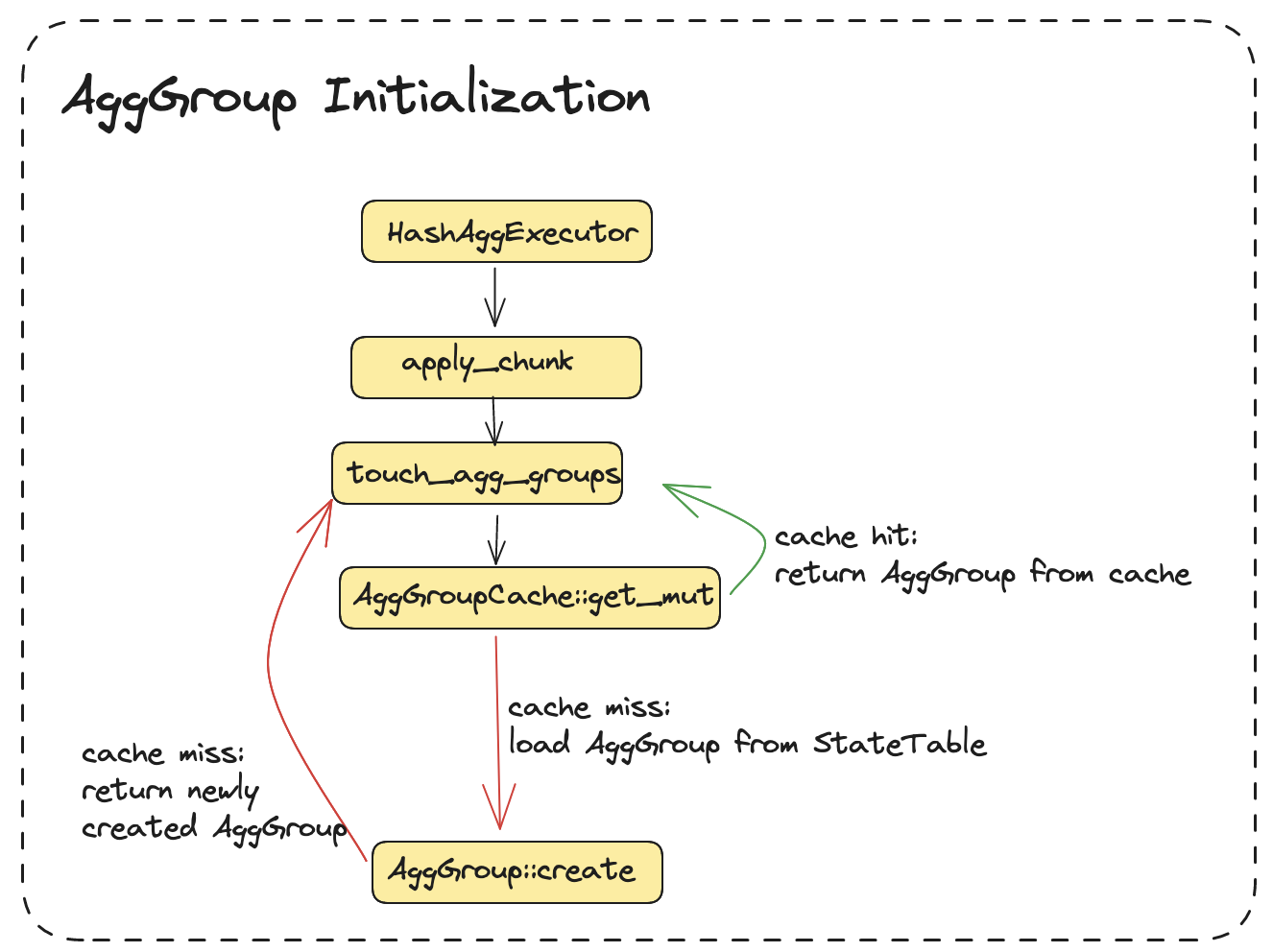
AggGroups are initialized when corresponding aggregation groups are not found in AggGroupCache.
This could be either because the AggGroupCache got evicted,
or its a new group key.
It could take a while to initialize agg groups, hence we cache them in AggGroupCache.